“Harappan Economy and Technology: 5000 Years Old Innovations”
The Harappan culture (Indus Valley Civilization) was one of the world’s earliest urban civilizations. It flourished between approximately 3300 BCE and 1300 BCE, and its peak is considered to be 2600–1900 BCE. This civilization spanned mainly parts of present-day Pakistan, western India, and Afghanistan.
Key Features
1. Organized Urban Planning
A network of roads was laid out in the settlement system.
Brick houses were built with standardized bricks.
The city was divided into two zones—the upper fort area (citadel) and the lower city (lower city).
2. Advanced Drainage System
One of the world’s most efficient drainage systems.
Drainage from every house was connected to the main drains.
 |
Qutub Minar History Mystery |
 |
 |
Mystical Khajuraho – Where Sculptures Whisper Stories |
 |
 |
Jaisalamer Ka Fort- Rajeshtaan |
 |
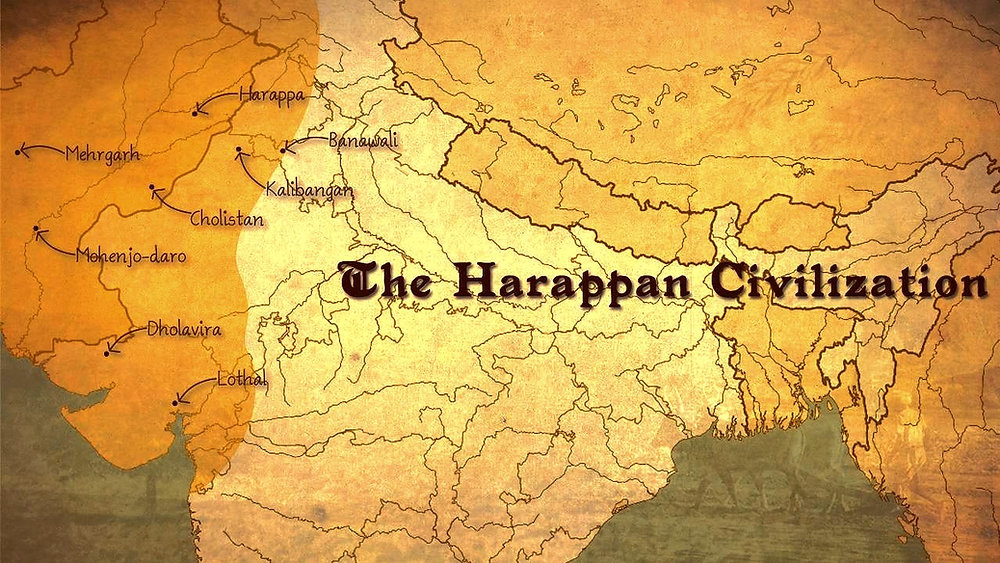
3. Important Sites
Harappa (Punjab, Pakistan) — First discovered site of the civilization
Mohenjo-daro — Great Bath, Uttarakhand city
Dholavira (Gujarat) — Advanced water management
Lotal (Gujarat) — Ancient dockyard
Kalibangan (Rajasthan) — Fire pit reservoir
Rakhigarhi (Haryana) — Largest Harappan site
4. Economic Life
Agriculture-based: wheat, barley, cotton (world’s earliest cotton users).
Trade: Trade with Mesopotamia (seals and beads).
Artwork: Beads, pottery, bronze objects.
5. Script and Language
The Harappan script remains undeciphered.
Animal figures and symbols are found on symbols.
6. Religious Beliefs
Evidence of Mother Goddess worship.
Animal worship—especially figures like bulls and unicorns.
Worship of vegetation and nature.
7. Causes of Decline (Possible)
Climate Change
Circulating Rivers (Ghaggar-Hakara)
Floods or Droughts
Decline in Trade
Importance
The Harappan culture was the first planned urban civilization in South Asia, laying the foundation for advanced architecture, urban life, and a trading network.

The Forbidden Forest Unexpected journey
God’s best creation “Earth” is about to end now! A terrible catastrophe is about to come! When on this earth created by God, that stick will be found which will create the earth anew…or end it! God has left his heaven and settled on earth! In the hope that the earth can be saved from those dark forces coming towards it! But the God of the earth! Man is still intoxicated by his scientific powers and is unaware of this catastrophe! Ever since this world was created! Just like life and death in the creation, light and darkness were also created at the time of creation of the universe! The feelings of truth, virtue, peace, benevolence and humanity must have risen with light! Then the dancing dark forces of untruth, unrest, discord and destruction must have made darkness their base! Man is the God of the earth! Those who are telling us about the life that existed on Earth thousands of years ago and the end of that life in the form of a great destruction by digging on the Earth with the help of their scientific powers and finding some small things and getting information about the past history! They do not know that the black powers of great destruction spread all around the universe have once again slowly spread on Earth! Man is ending truth and humanity by getting caught in the clutches of falsehood, sin, adultery and devilishness! Now he is moving towards his own end! Once again life on Earth will end! But this time the situation is different for us, that is, the black and devilish powers!
|
Harappan Civilization Timeline
1. Pre-Harappan Phase — 7000 BCE – 3300 BCE
Beginning of agriculture and animal husbandry in Mehrgarh (Balochistan) — around 7000 BCE
Development of mud houses, pottery, and early agricultural tools.
Gradual expansion of settlements and the beginning of the use of metal.
2. Early Harappan Phase — 3300 BCE – 2600 BCE
Development from villages to cities.
Increased use of mud bricks.
Emergence of sites like Dholavira, Kalibangan, Kot Diji, etc.
Increase in agricultural production, beginning of trade contacts.

3. Mature Harappan Phase — 2600 BCE – 1900 BCE
Golden Age of Civilization
Organized town planning, drainage, development of forts and lower cities.
Mohenjo-daro, Harappa, Dholavira, Lothal, and Rakhigarhi were the most developed cities.
Cotton production, bead production, brick houses, grain storage, and expansion of maritime trade.
Seals, script, bronze figurines (e.g., Dancing Girl).
 |
Age 30+ best exercise makes you stronger |  |
 |
Age 30+ which food makes you younger? |
 |
 |
Best yoga for 30 to 50 age. |  |
4. Late Harappan Phase – 1900 BCE – 1300 BCE
Decline of cities and return to rural life.
Floods, droughts, river diversions, and reduced trade.
Case of activity in some areas of Kalibangan and Lothal.
Beginning of the Painted Grey Ware (PGW) culture in the Punjab-Haryana region.
5. Final Phase/Extinction – 1300 BCE After
Major cities were abandoned.
Remnants of the Harappan culture remained only in small villages.
The Rise of New Civilizations—Vedic Culture Dominant.
Brief Timeline Table
Phase Period: Main Characteristics
Pre-Harappan 7000–3300 BCE: Mehrgarh, Beginning of Agriculture
Early Harappan 3300–2600 BCE: Beginning of Cities, Unbaked Bricks
Mature Harappan 2600–1900 BCE: Highly Urbanized Culture, Trade
Late Harappan 1900–1300 BCE: Decline, Ruralization
Last Phase: The End of the Civilization After 1300 BCE
Harappan Culture and Science (Science & Technology in Harappan Civilization)
The Harappans were highly advanced in many fields of science and technology. Their scientific understanding is clearly visible in town planning, construction, metallurgy, water management, calculation systems, and environmental knowledge. A detailed description is given below—
 |
Disadvantages of getting angry |  |
 |
How to stay fit at the age of 30+ |  |
 |
Natural way to brighten your skin |  |
1. Urban Planning Science
Harappan cities are considered among the most well-organized ancient cities in the world.
Key Scientific Features—
Grid Pattern—Construction of roads intersecting at 90° angles.
Zoning Technique—Dividing the city into a fortified upper and lower part.
Roads were built according to wind direction and sunlight.
Standardization of bricks (1:2:4 ratio)—This reflects mathematical and architectural knowledge.
2. Water Management and Drainage (Hydraulics & Water Engineering)
Scientific Achievements—
The world’s most advanced drainage system.
Covered drains, which were provided with manholes for periodic cleaning.
Rainwater Harvesting Technique at Dholavira.
The world’s first dockyard at Lotal—knowledge of water flow and ocean tides.
3. Metallurgy
The Harappans were quite advanced in the use of metals.
Main metals—
Copper, bronze, lead, tin, gold, and silver.
They knew the technique of making alloy bronze, which is a significant scientific achievement.
Example—
Bronze statue of a ‘Dancing Girl’
Metal tools, weapons, mirrors, knives, and jewelry
4. Measurement, Weights & Mathematics
The Harappans developed standardized weights and measures.
Scientific Features—
Accuracy in making weights, mostly chert stone weights.
Units were linked to a decimal-like system.
Graduated stone slabs for measuring length have been found (Lothal, Mohenjo-daro).
→ This demonstrates knowledge of mathematics and geometry.
5. Architecture & Civil Engineering
Large-scale use of baked bricks —scientific understanding of temperature control.
Multi-story buildings —sound foundations and knowledge of load distribution.
Scientific construction of granaries —ventilation systems.
6. Medicine & Human Knowledge
Evidence of tooth drilling at Mehrgarh—an example of early dentistry.
Knowledge of bones and medicinal plants.
Signs suggestive of surgical procedures have been found on some skeletons.
7. Environmental Science
Settlement along rivers, flood control measures.
Water harvesting at Dholavira was climate-friendly—this demonstrates an understanding of the environment.
Scientific use of river water and soil quality in agriculture.
8. Textile Technology
Cotton was first used here in the world.
Advanced dyeing and weaving techniques.
9. Navigation & Maritime Knowledge
The Lotal dockyard is a testament to their excellent understanding of marine science.
Scientific techniques for measuring water levels and stabilizing ships.
Conclusion
The Harappan culture was a civilization that laid the early foundations of many areas of modern science and technology.
Their scientific achievements demonstrate that even nearly 4,000 years ago, highly developed technical, mathematical, water management, and metallurgical knowledge existed in the Indian subcontinent.
How old is the Harappan culture, economy, and science?
The Harappan Civilization (Indus Valley Civilization) is believed to be approximately 7,000 years old. It developed in several phases—and the development of the economy and science also followed these phases.
 |
Cheek It Up Blush swiss beauty |
 |
 |
Matte Lip Palette swiss beauty |
 |
 |
Non-transfer Matte Lipstick swiss beauty |
 |
 |
Pure Matte Lipstick swiss beauty |
 |
1. Pre-Harappan Period—from 7000 BCE
Approximately 9,000–8,000 years old.
The beginnings of agriculture, animal husbandry, and early science in Mehrgarh.
2. Early Harappan Period—from 3300 BCE
Approximately 5,300 years old.
The move from villages to cities, the foundation of industry and trade.
3. Mature Harappan Period—2600–1900 BCE
This was the golden age of Harappan economy and science.
This period is 4,600–3,900 years old.
During this time, advanced town planning, trade, metallurgy, drainage systems, and scientific achievements were at their peak.
4. Post-Harappan Period—1900–1300 BCE
3900–3300 years ago.
Economic decline and decline of science and technology.
In simple terms,
The Harappan culture was an advanced urban civilization approximately 4,600 years old.
Its scientific achievements (drainage, mathematics, metallurgy, town planning)
and economy (agriculture, industry, trade) flourished approximately 2600–1900 BCE.
Conclusion
The Harappan economy and scientific advancements are approximately 4,000–4,600 years old.
The entire culture (including pre-Harappan) is believed to be approximately 7,000 years old.
Note: What are your thoughts on ” Harappan 5000 Years Old Innovations?” Please let us know in the comments section below. Your opinion is very important to us.
 |
UFO™ 3 (Reduce the look of wrinkles in 1 week) |
 |
 |
BEAR™ 2 (Safe, painless, non-invasive alternative to surgery) |
 |
 |
FAQ™ 301 (Red light therapy for hair growth) |
 |
 |
LUNA™ 4 hair |
 |




Если вы планируете поездку в Калининград и любопытствуете, какое море омывает населённый пункт, то это, разумеется, Балтийское море. Немало людей спрашивают, можно ли купаться в Балтийском море в Калининграде — ответ меняется в зависимости от времени года и температуры воды, которая летними днями с трудом поднимается выше 18–20 градусов. Но при этом, купальный сезон в Калининграде традиционно начинается с июня и тянется до августа, а в более нежаркие месяцы лучше выйти на пеший маршрут по прекрасным районам, например, по Амалиенау или в знаменитый Танцующий лес на Куршской косе.
Наряду с морских наслаждений, в Калининграде следует посетить органный концерт в кафедральном соборе — здесь установлен самый большой орган в России, а билеты легко приобрести по ссылке калининград что посмотреть . Для родителей с детьми интересным будет калининградский городской зоопарк, где можно оформить билеты заранее, а также музей янтаря и Рыбная деревня — замечательные места, чтобы узнать, чем знаменит Калининград и что посетить за пару дней. Не забудьте проверить прогноз погоды в Калининграде, в частности если планируете поездку в октябре или в зимний период — климат здесь благоприятный, но целесообразнее подготовиться!